Updated Cyber Essentials Requirements From March 1st 2017

The National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) has released the latest requirements for Cyber Essentials.
These are changes or enhancements from the old requirements, and highlight the following:
Scope
The requirements apply to all the devices and software that are within this boundary and that meet the conditions below:
- accept incoming network connections from untrusted Internet-connected hosts.
- establish user-initiated outbound connections to arbitrary devices via the Internet.
- control the flow of data between any of the above devices and the Internet.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) configurations are now in scope as the Applicant has control of the ope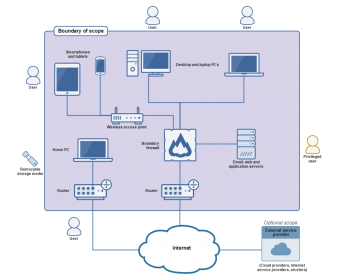 rating systems on the infrastructure.
rating systems on the infrastructure.
Software as a Service (SaaS) and Platform as a Service (PaaS) are not in scope.
Wireless devices (including wireless access points) are:
- in scope if they can communicate with other devices via the Internet.
- not in scope if it is not possible for an attacker to attack directly from the Internet.
Bring your own device (BYOD)
In addition to mobile or remote devices owned by the organisation, user-owned devices which access organisational data or services are in scope.
Password Requirements.
- The requirement to change admin passwords on a regular basis (at least every 60 days) has been removed.
- The requirement that passwords be promptly changed if the applicant knows or suspects they have been compromised has been added.
- The requirement for password lockouts or timeouts has been added. This limits the risk of brute force attacks on accounts and will:
- lock accounts after no more than 10 unsuccessful attempts
- limit the number of guesses allowed in a specified time period to no more than 10 guesses within 5 minutes
- You should have a password policy that tells users:
- how to avoid choosing obvious passwords (such as those based on easily-discoverable information like the name of a favourite pet).
- not to choose common passwords — this could be implemented by technical means, e.g. using a password blacklist.
- not to use the same password anywhere else, at work or at home.
- where and how they may record passwords to store and retrieve them securely — e.g. in a sealed envelope in a secure cupboard.
- if they may use password management software — if so, which software and how?
- which passwords they really must memorise and not record anywhere.
Patch Management Requirements.
Software must be:
- licensed and supported,
- removed from devices when no longer supported,
- patched within 14 days of an update being released, where the patch fixes a vulnerability with a severity the product vendor describes as 'critical' or 'high risk'
For the purposes of the Cyber Essentials scheme, 'critical' or 'high risk' vulnerabilities are those with the following values:
- attack vector: network only
- attack complexity: low only
- privileges required: none only
- user interaction: none only
- exploit code maturity: functional or high
- report confidence: confirmed or high
Malware Protection Requirements.
Devices in scope must have one of the following mechanisms
Anti-malware software
- The software (and all associated malware signature files) must be kept up to date, with signature files updated at least daily.
- The software must be configured to scan files automatically upon access.
- The software must scan web pages automatically when they are accessed through a web browser (whether by other software or by the browser itself).
- The software must prevent connections to malicious websites on the Internet (by means of blacklisting, for example) — unless there is a clear, documented business need and the Applicant understands and accepts the associated risk.
Application whitelisting
- Only approved applications, restricted by code signing, are allowed to execute on devices. The Applicant must:
- actively approve such applications before deploying them to devices.
- maintain a current list of approved applications.
- Users must not be able to install any application that is unsigned or has an invalid signature.
Application sandboxing
- All code of unknown origin must be run within a 'sandbox' that prevents access to other resources unless permission is explicitly granted by the user. This includes:
- other sandboxed applications,
- data stores, such as those holding documents and photos,
- sensitive peripherals, such as the camera, microphone and GPS,
- local network access.
Firewall Requirements
- Requirement for remote access must be protected by a second authentication factor, such as:
- a one-time token,
- an IP whitelist that limits access to a small range of trusted addresses.
- Use a host-based firewall on devices which are used on untrusted networks, such as public Wi-Fi hotspots.
- Ensure inbound firewall rules are approved and documented by an authorised individual; the business need must be included in the documentation
Click here for a full list of requirements on the NCSC website
If you have any questions or would like to book an assessment please contact us.